There are more and more electronic devices in our daily life, and they all require some form of power supply to function properly. Fortunately, there are many forms of energy around us, which can convert wind energy, light energy, kinetic energy of objects into electrical energy, and even harvest some energy from the transmission of high-frequency radio signals.
Less common but rapidly gaining popularity is the energy harvesting scheme from RF/microwave signals, which can be harvested from radio/television broadcast stations and wireless devices. This energy harvesting scheme can replace batteries in low-power applications such as Internet of Things (IoT) sensors and radio frequency identification (RFID) tags. Reusing energy reduces operating costs and increases the energy efficiency of existing electronic systems and equipment.
RF is a rich source of energy harvesting, and it is being emitted from billions of radio transmitters around the world, including mobile phones, mobile phone base stations, and TV/radio signal transmission base stations. Therefore, it has become a trend to use RF energy to power some low-power circuits.
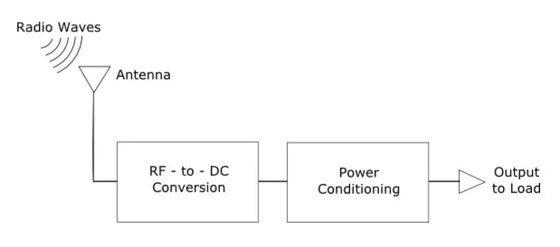
The concept of harvesting energy from RF is not new, and the process is relatively simple. Radio waves reach the antenna and cause a change in potential difference across its length. This potential difference causes the charge carriers to move along the length of the antenna in an attempt to equalize the field, and the RF-DC integrated circuit is able to capture energy from the movement of these charge carriers. The energy is temporarily Stored in the capacitor and then used to create the required potential difference at the load.
The RF energy signal is received through the antenna, so the operating frequency of the antenna must be the same as the frequency of the received signal. After the RF signal is received through the antenna, it can be used in both RF-DC converters and pure RF applications; The RF-DC converter converts the RF signal into a DC signal, so that the obtained energy can be stored in an energy storage device; the energy storage device can provide energy for RF-DC converters, RF devices, and low-power applications.
A circuit can be created to perform RF-to-DC conversion for the subsystem with off-the-shelf components. Utilizing various combinations of antennas, wireless charging coils, PMICs (power management ICs), power receiver chips, exciter transmitters, etc. can create systems capable of harvesting energy from RF.
The RF energy signal is received through the antenna, so the operating frequency of the antenna must be the same as the frequency of the received signal. After the RF signal is received through the antenna, it can be used in both RF-DC converters and pure RF applications; The RF-DC converter converts the RF signal into a DC signal, so that the obtained energy can be stored in an energy storage device; the energy storage device can provide energy for RF-DC converters, RF devices, and low-power applications.
Contact: Adam
Phone: +86 18205991243
E-mail: sale1@rfid-life.com
Add: No.987,Innovation Park,Huli District,Xiamen,China